
Please Wait...
Pass4Future also provide interactive practice exam software for preparing HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Professional (HPE7-A01) Exam effectively. You are welcome to explore sample free HPE7-A01 Exam questions below and also try HPE7-A01 Exam practice test software.
Do you know that you can access more real HPE7-A01 exam questions via Premium Access? ()
A network engineer recently identified that a wired device connected to a CX Switch is misbehaving on the network To address this issue, a new ClearPass policy has been put in place to prevent this device from connecting to the network again.
Which steps need to be implemented to allow ClearPass to perform a CoA and change the access for this wired device? (Select two.)
Answer : B, C
To trigger CoA for a specific wired device, the network engineer needs to bounce the switchport, which is an action that temporarily disables and re-enables the port where the device is connected. This forces the device to reauthenticate and receive the new policy from ClearPass. Bouncing the switchport can be done manually by using the interface shutdown and no shutdown commands, or automatically by using ClearPass as a CoA server and sending a RADIUS message with the Port-Bounce-Host AVP (Attribute-Value Pair).
Your Director of Security asks you to assign AOS-CX switch management roles to new employees based on their specific job requirements. After the configuration was complete, it was noted that a user assigned with the auditors role did not have the appropriate level of access on the switch.
The user was not allowed to perform firmware upgrades and a privilege level of 15 was not assigned to their role. Which default management role should have been assigned for the user?
Answer : B
The correct answer is B. sysops.
The other options are incorrect because:
A customer just upgraded aggregation layer switches and noticed traffic dropping for 120 seconds after the aggregation layer came online again. What is the best way to avoid having this traffic dropped given the topology below?
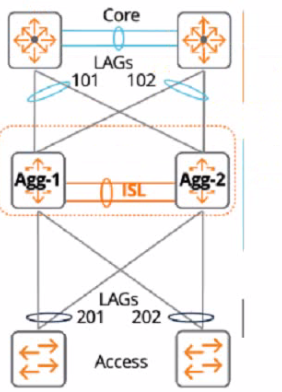
Answer : C
The reason is that the linkup delay timer is a feature that delays bringing downstream VSX links up, following a VSX device reboot or an ISL flap. The linkup delay timer has two phases: initial synchronization phase and link-up delay phase.
The initial synchronization phase is the download phase where the rebooted node learns all the LACP+MAC+ARP+STP database entries from its VSX peer through ISLP. The initial synchronization timer, which is not configurable, is the required time to download the database information from the peer.
The link-up delay phase is the duration for installing the downloaded entries to the ASIC, establishing router adjacencies with core nodes and learning upstream routes. The link-up delay timer default value is 180 seconds. Depending on the network size, ARP/routing tables size, you might be required to set the timer to a higher value (maximum 600 seconds).
When both VSX devices reboot, the link-up delay timer is not used.
Therefore, by configuring the linkup delay timer to include LAGs 101 and 102, which are part of the same VSX device as LAG 201, you can ensure that both devices have enough time to synchronize their databases and form routing adjacencies before bringing down their downstream links.
A company recently upgraded its campus switching infrastructure with Aruba 6300 CX switches. They have implemented 802.1X authentication on edge ports where laptop and loT devices typically connect An administrator has noticed that for PoE devices the pons are delivering the maximum wattage instead of what the device actually needs Upon connecting the loT devices, the devices request their specific required wattage through information exchange
Answer : D
A customer has a site with 200 AP-515 access points 75AP-565 access points installed. The customer is rolling out new mobile phones with Wi-Fi-calling. 802.1X is in use for authentication
What should be enabled to ensure the best roaming experience?
Answer : A
Wi-Fi calling is a feature that allows you to make or receive voice calls over Wi-Fi instead of cellular network. Wi-Fi calling can provide better voice quality and reliability in areas with poor or no cellular coverage.